How to Check Air Quality in Home? Tips From Experts
Key Takeaways
- A home air quality test identifies specific pollutants and their exact concentrations.
- Common contaminants include PM2.5 particulates, VOCs, CO2, mold spores, carbon monoxide, and radon.
- Physical symptoms like persistent headaches, congestion, and fatigue often point to contaminated indoor air.
- Continuous monitoring with an air quality sensor for home catches problems that one-time tests miss completely.
- Knowing your specific pollutants lets you fix the right things instead of guessing.
Nearly 90% of your time happens indoors, yet the air inside your house can run two to five times more polluted than the street outside. You can't see particles, gases, mold spores, or chemical vapors floating through every room. A home air quality test gives you real numbers about what's contaminating your living space, so you stop guessing why you wake up congested or why allergies flare up every winter.
Why Should You Check Air Quality at Home?
Your home traps what it can't push out. Every time you fry an egg, tiny particles launch into the air. Your new couch releases chemical vapors for years after purchase. Cleaning products leave volatile compounds lingering long after you've put them away. And every person in your household exhales CO2 constantly, all day and all night.
Sealed buildings make all of this worse. Modern construction keeps energy bills low. But tight building envelopes also keep pollutants locked inside with nowhere to go.
Research published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health connects poor indoor air to roughly $2,500 in annual healthcare expenses per American household. Headaches that won't quit. Chronic fatigue you can't explain. Respiratory irritation that comes and goes. These symptoms trace back to invisible airborne contaminants sitting right in your living room more often than most doctors realize.
Here's where indoor air quality testing pays off. Once you have measurements, you stop guessing. Maybe your bedroom CO2 spikes dangerously high overnight because ventilation falls short. Or PM2.5 triples every time you use your gas stove. Or radon has been seeping through foundation cracks for years without anyone noticing. Numbers tell you exactly what to fix.
Common Indoor Air Pollutants
Different pollutants demand different detection methods and different fixes. Knowing what might lurk in your air helps you pick the right air quality test approach.
Particulate matter measuring 2.5 micrometers or smaller penetrates deep into lung tissue. Some particles even cross into your bloodstream. The World Health Organization connects PM2.5 to cardiovascular disease, respiratory infections, stroke, and premature death. Cooking generates enormous amounts, especially frying and grilling. Candles, fireplaces, smoking, and outdoor pollution sneaking through your walls all contribute.
VOCs evaporate from paints, varnishes, cleaning products, air fresheners, new furniture, carpeting, and building materials. Formaldehyde, benzene, toluene. Short-term exposure triggers eye and throat irritation, headaches, nausea. Years of breathing these compounds? That's when cancer risk climbs. Formaldehyde earned its classification as a known human carcinogen for good reason.
Carbon dioxide accumulates fast in bedrooms overnight, especially with doors closed. Anything above 1,000 ppm makes you drowsy and unfocused. Push past 2,000 ppm and you'll notice headaches, difficulty concentrating, measurable drops in cognitive performance. Some poorly ventilated bedrooms hit 3,000 ppm by morning. No wonder you feel groggy waking up.
Mold thrives anywhere moisture collects. Bathrooms, basements, crawl spaces. Spores travel through HVAC systems and spread throughout your entire house. They trigger allergic reactions, asthma attacks, respiratory infections. Dust mites, pet dander, bacteria, and viruses add to the biological contamination load.
Carbon monoxide escapes from gas appliances, wood-burning fireplaces, attached garages, malfunctioning heating equipment. Low levels mimic flu symptoms. High concentrations kill within hours.
Radon seeps through the soil beneath your foundation. The EPA calls it the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, responsible for roughly 21,000 American deaths annually. You can't smell it, see it, or taste it. Only indoor air quality testing reveals its presence.
|
Pollutant |
Where It Comes From |
Health Effects |
When To Worry |
|
PM2.5 |
Cooking, candles, outdoor air |
Heart disease, lung damage |
Above 35 µg/m³ |
|
VOCs |
Paint, cleaners, furniture |
Eye irritation, cancer risk |
Above 500 ppb |
|
CO2 |
Breathing, combustion |
Brain fog, fatigue |
Above 1,000 ppm |
|
Carbon Monoxide |
Gas appliances, garages |
Poisoning, death |
Above 35 ppm |
|
Radon |
Soil through foundation |
Lung cancer |
Above 4 pCi/L |
|
Mold |
Moisture-prone areas |
Allergies, infections |
Visible growth or musty smell |
Signs of Poor Indoor Air Quality
Your body reacts to contaminated air before any test confirms the problem. Pay attention. These signals mean something.
Location patterns tell you everything. Does your coughing improve when you leave for work? Does congestion return the moment you walk through your front door? Sinus pressure that vanishes on vacation but reappears at home? That pattern screams indoor air problems louder than any sensor could.
Unexplained brain fog raises red flags too. Feeling sharp at the office but mentally sluggish at home suggests elevated CO2, VOCs, or carbon monoxide in your living space. The contrast itself becomes your biggest clue.
Your nose knows more than you'd expect. Musty odors mean mold. Persistent chemical smells indicate high VOC concentrations. Stale, stuffy air suggests ventilation has failed and CO2 keeps climbing. Condensation on windows shows humidity running too high.
For more about how bad air affects your health, check out our detailed breakdown on what are the symptoms of bad air quality.
How to Test Air Quality in Your Home
 Indoor air quality testing ranges from free observations to professional assessments costing several hundred dollars. The right approach depends on what concerns you most.
Indoor air quality testing ranges from free observations to professional assessments costing several hundred dollars. The right approach depends on what concerns you most.
Start With Your Own Senses
Walk through your house like a detective. Your body already knows more than you realize.
Sniff around. Musty basement smell probably means mold. Chemical odor in the newly renovated room? VOCs off-gassing from paint or flooring. Stale air everywhere? Ventilation problems letting CO2 accumulate.
Look carefully at walls and ceilings. Black or green spots suggest mold colonies. Excessive dust coating air vents indicates filtration failures. Water stains hint at moisture problems. Fog on windows every morning means humidity has climbed too high.
Track your symptoms for a week. Write down when you feel worst and where.
Test Kits and Detectors
Radon and mold test kits capture snapshots of specific pollutants. Place them according to instructions, wait 48 to 96 hours for radon tests, then mail samples to a lab. Prices run $15 to $50. Works great when you already suspect a specific problem.
Carbon monoxide detectors belong in every home with gas appliances. Period. Any positive reading demands immediate action. Get everyone out and call your gas company.
Continuous Monitoring
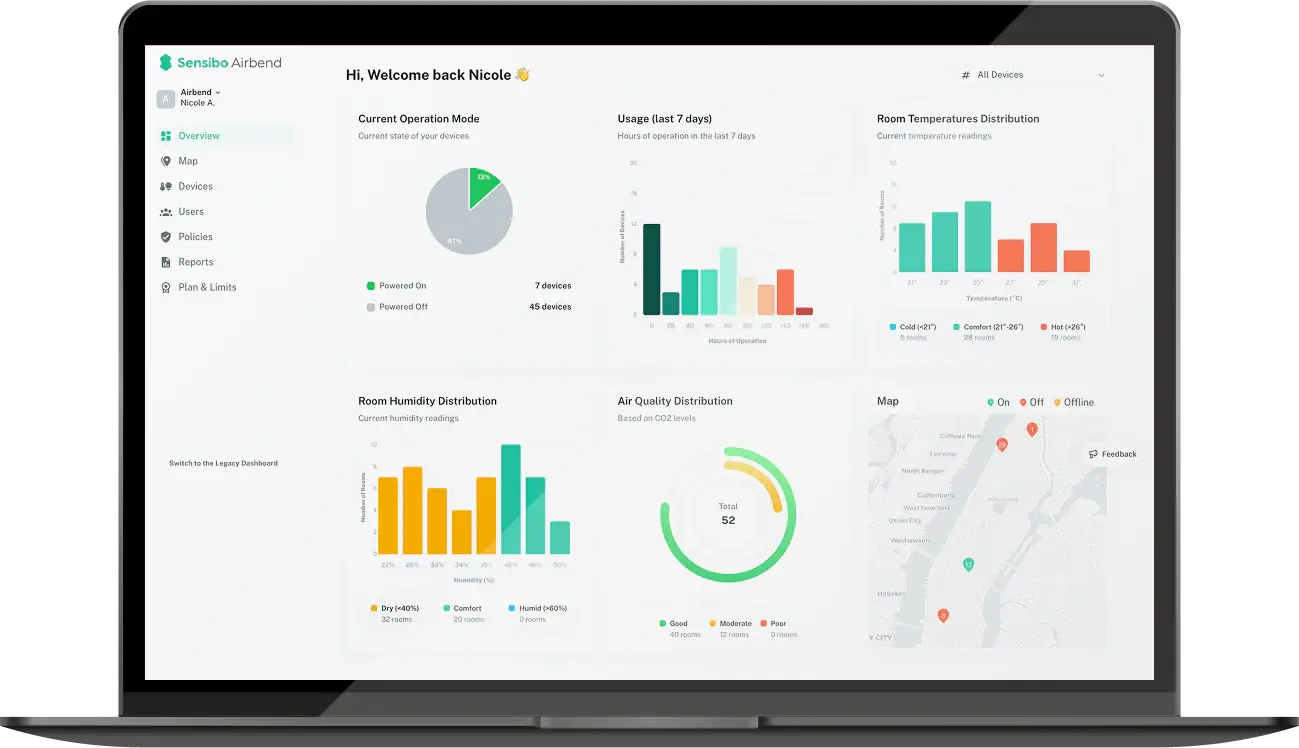
An air quality sensor for home use tracks PM2.5, CO2, VOCs, temperature, and humidity around the clock. Sensibo Elements monitors all these metrics continuously, showing you exactly what happens in your air throughout the day.
Patterns emerge that single tests would never reveal. Maybe PM2.5 spikes every evening when your neighbor burns wood. Or CO2 climbs steadily through dinner parties. Real-time monitoring catches what one-time testing misses completely.
Professional Assessment
Certified specialists bring laboratory-grade equipment capable of identifying specific pollutant species and precise concentrations. They test for mold with species identification, asbestos, lead dust, formaldehyde, radon, and dozens of individual VOCs. Expect to pay $300 to $700 for thorough assessment.
Worth every penny if you suspect serious contamination or need documentation for insurance. Avoid companies that both test and remediate.
How to Improve Indoor Air Quality
 Your test results tell you exactly where to focus. Generic advice wastes money. Targeted interventions based on your specific data deliver results.
Your test results tell you exactly where to focus. Generic advice wastes money. Targeted interventions based on your specific data deliver results.
Source Control and Ventilation
Removing contamination beats filtering contaminated air. Store household chemicals in sealed containers or outside living spaces. Swap high-VOC paints for low-VOC alternatives. Throw away synthetic air fresheners. They add VOCs while masking other odors.
Fix water leaks within 48 hours. Mold colonizes fast once moisture appears. Never idle your car in an attached garage.
Open windows when outdoor air quality permits. Run bathroom exhaust fans during and after showers. Use kitchen range hoods that vent outside.
Filtration
Upgrade HVAC filters to MERV 13 or higher for effective fine particle capture. Replace every 60 to 90 days. More frequently with pets.
A smart air purifier connected to air quality sensors activates when pollution rises. No manual intervention required. For VOC reduction, choose purifiers with activated carbon filters alongside HEPA.
Humidity and Specific Problems
Target 30% to 50% relative humidity. Below 30% irritates airways. Above 50% accelerates mold growth. Run dehumidifiers in moisture-prone spaces.
High radon above 4 pCi/L requires a mitigation system, typically $800 to $1,500 installed. Mold under 10 square feet you can clean yourself. Larger areas need professionals. Elevated carbon monoxide means getting combustion appliances inspected immediately.
Maintaining Air Quality Long-Term
Check your air quality sensor readings daily. Make it routine. Note patterns and anomalies. If PM2.5 spikes every Tuesday evening, figure out why.
Mark your calendar for HVAC filter changes. Homes with pets or high outdoor pollution need changes more frequently.
Each season brings different challenges. Spring means pollen infiltration. Summer humidity encourages mold. Fall brings heating system startup dust. Winter seals homes tight, trapping pollutants and letting CO2 climb.
Family members with respiratory conditions benefit when you track air quality alongside symptoms. Your doctor can make better treatment decisions with that data.
FAQ
How often should I test my home's air quality?
Continuous monitoring gives the most complete picture since air quality changes constantly. Test radon every two years or after major renovations. Test for mold after water damage or when musty odors appear. Check CO detector batteries monthly.
What counts as good indoor air quality?
PM2.5 below 12 µg/m³, CO2 under 1,000 ppm, total VOCs below 500 ppb, humidity between 30% and 50%, zero carbon monoxide, radon below 4 pCi/L. Indoor mold spore counts should roughly match outdoor levels.
Can houseplants clean your air?
Real-world effectiveness is minimal. You'd need hundreds of plants per room to match what one decent air purifier accomplishes. Enjoy plants for aesthetics and mood benefits. Don't count on them for air cleaning.
How much does professional indoor air quality testing cost?
Full assessments covering multiple pollutants run $300 to $700. Single-pollutant tests cost $150 to $300. DIY radon kits cost $15 to $50.
Do air purifiers work?
HEPA purifiers capture 99.97% of particles 0.3 microns and larger when properly sized for the room. Check Clean Air Delivery Rate and match it to your room volume. But purifiers don't address CO2, radon, or carbon monoxide. Those require separate approaches.

































.jpg?height=200&name=photo_2024-01-24_18-02-44%20(1).jpg)
.jpg?height=200&name=image6%20(2).jpg)

