Can Poor Air Quality Cause Headaches? All You Should Know
Key Takeaways
- Dirty indoor air cuts off oxygen to your brain while flooding it with toxic chemicals
- The worst culprits? VOCs from furniture, cooking particles, stuffy air, and hidden mold
Air quality headache warning signs: pounding temples, dead tired feeling, clogged sinuses
- Fast relief comes from fresh air, fans, and ditching whatever's causing the problem • Smart gadgets catch trouble before your head starts hurting
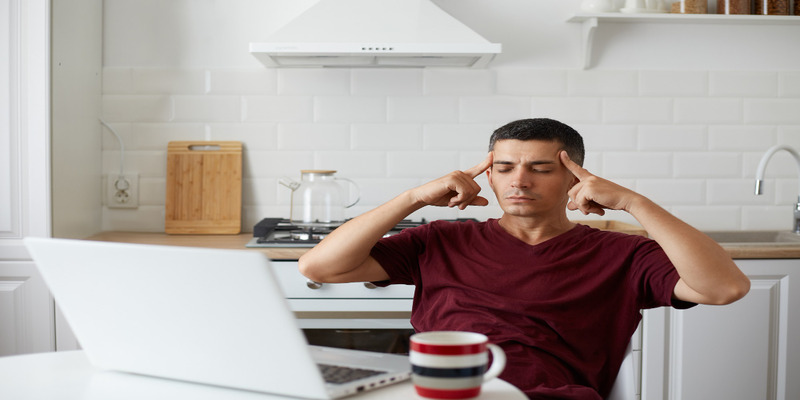
Can poor air quality cause headaches? Yes, it absolutely can. Bad indoor air hits your head harder than you'd expect. Most homes trap pollution at levels way higher than what's floating around outside. Once you understand what's happening, stopping those mystery headaches becomes much easier.
The Science Behind Air Quality and Headaches
Here's what happens when bad air meets your brain. Your noggin burns through one-fifth of all the oxygen you breathe. Pollutants mess with that delivery system while dumping inflammatory garbage into your blood.
Think of it like this: chemicals irritate your blood vessels, making them swell up. That swelling creates pressure and pain. Carbon dioxide from stale rooms makes your heart work overtime just to pump enough oxygen around.
But wait, there's more. Those same chemical fumes hit nerve endings in your nose and sinuses. Your body fights back by producing extra mucus. Now you've got sinus pressure on top of the blood vessel swelling. Double trouble.
Research proves that tiny increases in pollution can trigger headaches within half an hour. When multiple bad guys team up - say, cooking smoke plus cleaning fumes plus poor ventilation - they pack a much bigger punch than working alone.
Common Indoor Air Pollutants That Trigger Headaches
Chemical Vapors That Sneak Around
New furniture gives off that distinctive smell because it's literally releasing chemicals into your air. Formaldehyde seeps out of anything made with pressed wood or particle board. Paint continues off-gassing for weeks after you finish the job. Even carpet glue keeps releasing vapors years later.
Those chemicals build up in closed spaces. No escape route means higher concentrations. Higher concentrations mean more headaches.
Tiny Particles Everywhere
Cooking creates more pollution than most people realize. Frying anything releases grease particles that stay airborne for hours. Candles look innocent but pump out ultrafine particles that drill deep into your lungs.
Pet dander floats around constantly. Dust mites shed microscopic pieces of themselves. Each type of particle triggers different reactions in your body.
Invisible Gases from Appliances
Gas stoves leak small amounts of carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide even when working perfectly. Furnaces with tiny cracks release more. Space heaters burn oxygen while producing combustion gases.
Carbon monoxide causes dull, persistent headaches long before reaching truly dangerous levels. Many people blame stress or lack of sleep when the real culprit is a slightly malfunctioning appliance.
Biological Troublemakers
Bathrooms grow mold behind tiles where you can't see it. Basements develop fungal colonies in damp corners. These living organisms release toxins that directly attack your nervous system.
Some people react to mold levels so low that others wouldn't notice. Individual sensitivity varies wildly.
Everyday Products Gone Wrong
Cleaning supplies leave residues that evaporate slowly throughout the day. Synthetic fabrics release processing chemicals. Air fresheners add their own volatile compounds while covering up other smells.
This creates constant, low-level exposure to headache from bad air quality triggers that accumulate over time.
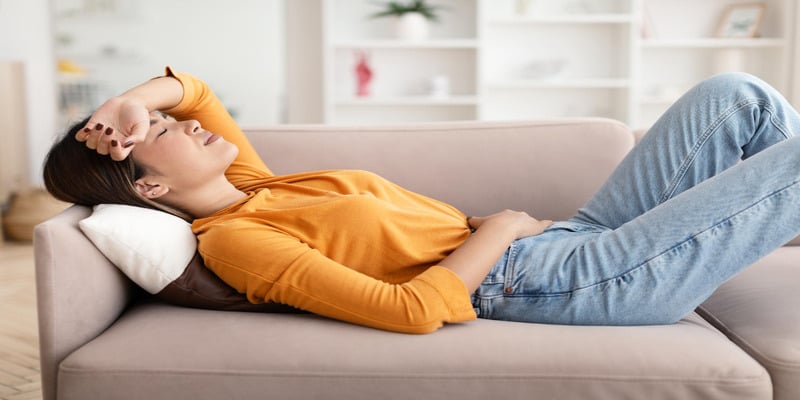
Recognizing Symptoms of Bad Air Quality Beyond Headaches
Symptoms of bad air quality rarely stop at just head pain. Your eyes usually complain first - burning, watering, getting red for no obvious reason.
Throat irritation follows close behind. Scratchy feeling, dry cough, wanting to clear your throat constantly. Your nose either stuffs up completely or runs like a faucet.
Mental fog creeps in as oxygen drops. Simple decisions become harder. Focusing on tasks takes more effort. You feel tired without doing anything strenuous.
Skin gets cranky too. Extra dryness, unexplained rashes, existing conditions getting worse for no clear reason.
Pay attention to timing patterns. Do symptoms hit hardest in certain rooms? Get better when you go outside? Worse during specific activities like cooking or cleaning? Those clues point straight to air quality problems.
Kids and older adults show symptoms fastest. Their respiratory systems either haven't fully developed or have started declining. Pregnant women often become hypersensitive to airborne irritants.

Room-by-Room Air Quality Culprits
Kitchen Chemical Factory
Gas burners shoot nitrogen dioxide straight up into your breathing space. High-heat cooking turns innocent cooking oil into acrolein - a major irritant. Self-cleaning ovens release chemical fumes intense enough to trigger smoke detectors.
That cabinet under your sink? It's probably packed with cleaning chemicals that leak vapors continuously. Garbage disposals grow bacteria that become airborne when you run them. Even your coffee maker contributes plastic-heated VOCs to the morning air.
Bedroom Pollution While You Sleep
Your mattress slowly releases flame retardant chemicals all night long. Breathing rate drops during sleep, allowing deeper penetration of whatever's floating around. Dust mites multiply in bedding, releasing allergenic particles with every toss and turn.
Closets stuffed with dry-cleaned clothes trap chemical residues from the cleaning process. Carpet padding underneath keeps off-gassing formaldehyde for years. Poor ventilation lets carbon dioxide build up while you're unconscious.
Bathroom Humidity Disasters
Weak exhaust fans can't keep up with shower steam. Moisture feeds mold growth in places you never see - behind tiles, under flooring, inside walls. Hot water releases chlorine vapor from municipal treatment chemicals.
Aerosol hair products and nail polish concentrate in small spaces with minimal air movement. Chemical toilet cleaners mixed with bathroom humidity create a perfect storm for respiratory irritation.
Living Room Pollution Sources
Particle board furniture continues leaking formaldehyde for the life of the piece. Electronics generate ozone while releasing flame retardants from heated plastic components. Leather furniture treated with chemicals emits those distinctive "new leather" smells - which are actually toxic vapors.
Even properly maintained fireplaces introduce combustion particles. Carpets absorb decades of chemical residues, pet accidents, and biological matter, then slowly release them back into your air.
How to Get Rid of Headaches Caused by Poor Air Quality
Emergency Escape Plan
How to get rid of headaches when they're already pounding starts with immediate evacuation. Step outside and breathe deeply. Relief often comes within 15-20 minutes once you escape the contaminated environment.
Race back inside and open every window possible. Create cross-ventilation by opening windows on opposite sides of your home. Turn on every exhaust fan you can find - bathroom, kitchen, laundry room, anywhere air moves.
Kill obvious pollution sources immediately. Blow out candles. Cap cleaning product bottles. Move away from areas where someone just finished using strong chemicals or doing messy cooking.
Quick Air Cleaning Tactics
Purification Arsenal:
- HEPA filters trap 99.97% of particles bigger than 0.3 microns
- Activated carbon absorbs chemical vapors and persistent odors
- UV lights kill biological nasties like mold spores and bacteria
Ventilation Power Moves:
- Box fans in windows create forced air exchange
- Attic fans suck hot, stale air out of your entire house
- HVAC systems with fresh air settings dilute indoor pollution
Source Elimination:
- Seal chemical containers and move them outside living areas
- Fix water leaks that feed mold colonies
- Toss heavily off-gassing items if replacement is possible
Prevention Through Technology
Air quality monitors warn you before symptoms start. These gadgets track particles, chemicals, and carbon dioxide in real-time. Many send smartphone alerts when levels spike above safe thresholds.
Smart versions connect to your heating and cooling system. When sensors detect rising pollution, they automatically increase ventilation rates or trigger air purifier operation.
Professional duct cleaning removes accumulated junk from your ventilation system. Years of dust, mold, pet dander, and chemical residues get sucked out, leaving clean pathways for fresh air circulation.
Smarter Product Choices:
- Low-VOC paints and finishes reduce chemical emissions
- Solid wood furniture skips formaldehyde from pressed wood
- Fragrance-free cleaning products eliminate unnecessary exposure
- Natural fiber fabrics avoid synthetic chemical off-gassing

Prevention Strategies and Long-term Solutions
Smart Home Air Defense
Modern technology transforms air quality management from reactive panic to proactive control. Sensors placed throughout your home communicate with ventilation equipment to maintain healthy conditions automatically.
Energy recovery ventilators solve the fresh air problem without energy waste. These systems bring outdoor air inside while capturing heating or cooling from exhaust air. Fresh air without crazy utility bills.
Whole-house air treatment systems handle everything flowing through your HVAC. Multiple technologies working together - HEPA filtration, carbon absorption, UV sterilization - provide comprehensive protection.
Seasonal Maintenance Routines
Hot Weather Preparation:
- Install higher-rated filters before pollen season hits
- Clean AC coils to prevent mold growth in humid conditions
- Test all exhaust fans before summer humidity arrives
- Service ventilation equipment before peak cooling demands
Cold Weather Getting Ready:
- Inspect heating equipment for carbon monoxide leaks
- Seal cracks that let outdoor pollution sneak inside
- Check fireplace and chimney venting before first use
- Monitor indoor humidity to prevent over-drying problems
Developing Air Quality Awareness
Schedule intensive cleaning projects when weather allows maximum window opening. Time cooking experiments for cool evenings when fresh air circulation works best. Establish chemical-free safe zones where sensitive family members can retreat during pollution episodes.
Annual professional maintenance catches problems before they trigger symptoms. HVAC tune-ups, ductwork cleaning, and quick equipment repairs maintain optimal performance throughout the year.
Understanding your home's unique pollution patterns helps you stay ahead of problems. Every house has different sources, timing, and seasonal variations.
Future Without Headaches
Can poor air quality cause headaches? Without question, and recognizing this connection changes everything. Those mysterious head pains finally make sense when you understand what's floating around in your indoor air.
Quick action often stops developing headaches cold. Fresh air, increased ventilation, and source removal work faster than most over-the-counter medications. Long-term monitoring and purification systems prevent future episodes entirely.
Start making changes today. Your head will feel better, and you'll probably notice other health improvements you never connected to air quality issues.
FAQ
How quickly can poor air quality cause headaches?
Some people develop headaches within 15 minutes of exposure, especially if pollution levels are high or they're particularly sensitive.
Can air purifiers really help with air quality headaches?
Good HEPA and carbon purifiers remove most headache triggers, often providing relief within 2-3 hours of continuous operation.
What's the ideal indoor air quality level to prevent headaches?
Keep carbon dioxide under 1000 ppm, humidity between 30-50%, and particle levels below 12 µg/m³ for best results.
Are some people more sensitive to air quality headaches than others?
Absolutely - kids, pregnant women, elderly people, and those with allergies or breathing problems react much faster to pollution.
How can I tell if my headache is from air quality or something else?
Air quality headaches usually improve when you leave the problem area and often come with burning eyes, stuffy nose, or scratchy throat.
Do expensive air quality monitors make a real difference?
Better monitors help pinpoint specific triggers and timing patterns, but basic monitoring still beats guessing what's wrong.

































.jpg?height=200&name=photo_2024-04-05_20-42-58%20(1).jpg)

.jpg?height=200&name=61545%20(1).jpg)
