Understanding Mildew: A Homeowners Guide to Air Quality and AC Maintenance
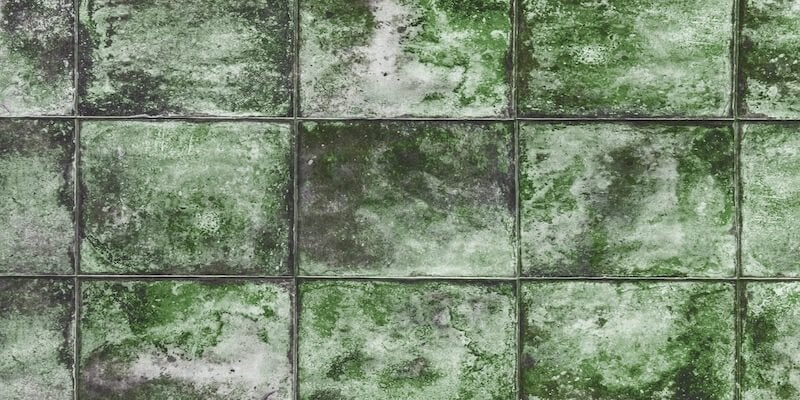

We spend 90% of our time indoors. As surprising as this statistic may be, it's, therefore, imperative to understand the various factors that can affect indoor air quality.
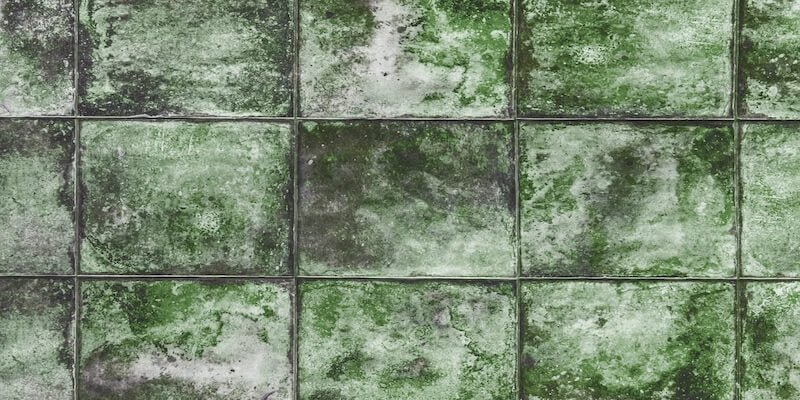
One common issue that can arise is the growth of mildew, a type of fungus that thrives in damp or humid environments. Mildew can grow on a variety of surfaces, including walls, ceilings, fabrics, and even air conditioning systems. It can release spores and other particles into the air, leading to allergic reactions and other health issues. In addition, mildew can cause physical damage to materials and surfaces, leading to costly repairs.
In this article, we explore what mildew is, how it grows, and how to prevent and remove it in air conditioning systems. By understanding mildew and taking steps to prevent and remove it, you can help keep your indoor spaces healthy and comfortable.
This article will cover the following topics:
- What is Mildew?
- How Does Mildew Grow?
- The Effects of Mildew on Indoor Air Quality
- Preventing Mildew in Air Conditioning Systems
- Removing Mildew from Air Conditioning Systems
- Mildew mitigation with Sensibo
What is Mildew?
Mildew is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid environments. It often appears as a white, gray, or black powdery substance on surfaces and has a musty, moldy smell.
Mildew can grow on a variety of surfaces, including walls, ceilings, fabrics, and even air conditioning systems. It thrives in warm, humid conditions and is often found in bathrooms, basements, and other areas with poor ventilation.
There are two main types of mildew: surface mildew and structural mildew. Surface mildew grows on the surface of materials and can be easily removed. Structural mildew, on the other hand, grows within the structure of materials and can cause significant damage if left unchecked.
How Does Mildew Grow?
Mildew grows when spores, which are tiny cells that contain the fungus's genetic material, land on a damp or humid surface. The spores then release enzymes that digest the surface they are growing on, allowing the mildew to spread.
Mildew requires three things to grow: a source of nutrients (such as dead plant matter or the cellulose in wood or paper), moisture, and warm temperatures. If these conditions are present, mildew can grow quickly and spread to other surfaces.
The Effects of Mildew on Indoor Air Quality
Mildew can have a negative impact on indoor air quality, as it releases spores and other particles into the air when it grows. These particles can be inhaled and can cause allergic reactions in some people, leading to symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing.
In addition to affecting air quality, mildew can also cause physical damage to surfaces and materials. It can weaken and deteriorate wood, plaster, and other building materials, leading to costly repairs.
Preventing Mildew in Air Conditioning Systems
Given the harm mildew may cause to your health, it's important to take steps to prevent mildew growth in your air conditioning units. Some steps you can take include:
- Maintaining proper humidity levels: Mildew thrives in humid environments, so it's important to keep indoor humidity levels between 30-50% to prevent growth. You can use a hygrometer to measure humidity levels and use a dehumidifier to reduce humidity if necessary.
- Cleaning and maintaining air conditioning systems: Regular cleaning and maintenance of air conditioning systems can help prevent the build-up of moisture and the growth of mildew. This includes cleaning or replacing air filters regularly and ensuring that the system is properly sealed to prevent leaks.
- Ventilating spaces: Proper ventilation can help prevent the build-up of moisture and the growth of mildew. Make sure that there is adequate ventilation in spaces with air conditioning systems, such as open windows or exhaust fans.
Removing Mildew from Air Conditioning Systems
If mildew has already formed in an air conditioning system, it's important to remove it as soon as possible to prevent further damage and improve indoor air quality. Here are some steps you can take to remove mildew from air conditioning systems:
- Turn off the system: Before attempting to remove mildew, it's important to turn off the air conditioning system to avoid any accidents or injuries.
- Clean the surface: Begin by cleaning the surface where the mildew is growing. Use a mixture of water and mild soap to wipe down the affected area, making sure to remove as much of the mildew as possible.
- Disinfect the area: After cleaning the surface, it's important to disinfect the area to kill any remaining spores. You can use a mixture of water and bleach or a commercial disinfectant to do this.
- Remove any damaged materials: If the mildew has caused significant damage to any materials, such as insulation or drywall, it may be necessary to remove and replace them.
- Repair any leaks or moisture issues: If the mildew was caused by leaks or moisture issues in the air conditioning system, it's important to repair these issues to prevent future growth.
Mildew mitigation with Sensibo
In conclusion, mildew is a common problem that can affect indoor air quality and cause damage to materials and surfaces. As a homeowner, it's important to understand the role of mildew in air quality and take steps to prevent and remove it in air conditioning systems. By maintaining proper humidity levels, cleaning and maintaining air conditioning systems, and ventilating spaces, you can help keep your indoor' spaces healthy and comfortable.
Having said that, proper mildew prevention and mitigation can be time-consuming, especially for those households that are employed full-time. That’s where the need for smart solutions like those provided by Sensibo come in. Their flagship product, Sensibo Air Pro, comes equipped with anti-mold functionality under which mildew is included. Visit Sensibo’s website to learn more.





































.jpg?height=200&name=photo_2024-01-05_17-53-34%20(1).jpg)